The adoption of the electric vehicles (EVs) is accelerating across Europe. And with this, the need for a proper EV charging infrastructure is rising. Within such an infrastructure, different type of EV chargers should be available. In this article, we’ll tell you everything you need to know about EV chargers.
First, we’ll explain the difference between AC & DC chargers. Then we will show you what the different type of charging possibilities there are as well as the types of plugs across the globe. And finally, we will look into two chargers specifically designed for electric fleet or electric heavy transport.
What are AC chargers & DC chargers?
In short, the difference lies in the way an electric vehicle is charged. EVs can be charged in two ways: AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current). The power available from the grid, is AC. However, Batteries can only store electricity with a direct current. So, to store power into the EV’s battery, a converter needs to change the electricity from AC to DC.
AC chargers are usually slower chargers, charging the battery at a slower, but steadier pace. DC chargers are most commonly fast chargers, charging the battery from 0% to 80% at a rapid pace. This difference has to do with where the conversion from AC to DC takes place.
When an EV is charged with an AC charger, this conversion happens inside the vehicle. This allows for a simpler AC Charger or a Wallbox. However, the power is limited due to the size of the converter integrated in the car. With DC charging, the conversion takes place within the charger itself. DC chargers are therefore bigger and more expensive, but it comes with the benefit that far more power can be delivered to the vehicle. In the image below, this difference is visually shown.
Next to the place of conversion and the power delivered, there are more differences between AC and DC chargers. For example, DC chargers obtain more information from the battery than AC chargers and can provide a better estimation of remaining time of charging.

When EVs were just introduced to the market, there was an exceptionally large lack of DC chargers. Charging at home (with a slow-paced AC charger) was most common. EV producers therefore provided bigger on-board chargers (or converters) inside the EV. For example: Renault Zoe used to charge up to 22, and even 44kW, without a DC charging capability. With the relatively small size of the battery of this early time, this solution was quite suitable.
The market has now shifted towards larger battery cars with more autonomy, requiring faster charging. Resulting in an increase in public DC chargers. With this trend, most EV cars now include both AC as well as DC charging capabilities. AC on-board chargers are now getting smaller and more cost effective, usually in the range of 7kW or 11kW, resulting in lower purchasing prices of EVs.
The different EV Charging possibilities
As explained, the speed of charging depends on the electric current (AC or DC). But other factors also influence the speed of charging, such as: the power of the charger and the power an EV can handle. This means if you charge your EV with at a charger of 100 kW and your vehicle can only handle 50 kW, the EV will charge at 50 kW.
The image below gives an overview of the different EV charging possibilities and an indication of the charging speed per type.

Domestic or workplace chargers are slower chargers. Slow charging is most commonly used for places where EV drivers can charge their car overnight or for about 8 hours or more. This could be at home, at the office or for example at a hotel. These chargers are almost always AC chargers.
Public chargers fully charge a vehicle in a few hours and are therefore typically placed at destinations where drivers tend to park their car for a several hours. Such as public parking places, shopping centres, and restaurants. Public chargers are usually AC chargers as well, but it’s not uncommon to mix AC chargers with DC chargers in these places.
Fast chargers can be used in many different situations. They are, just like public chargers, typically installed at places such as shopping centres and restaurants. Car dealerships also often provide visitors with an option of fast charging. Fast chargers are also seen at service stations, which is ideal for EV drivers with smaller batteries.
Ultra-fast chargers and High-Power-Chargers (HPC’s) are the quickest way to charge an EV and are therefore perfect for service stations next to busy highways or close to main roads, ensuring EV drivers can complete their long journeys. These chargers are exclusively DC chargers and can charge an electric vehicle rapidly from 0% to 80%, typically in 20 to 40 min. Next to installations at existing service stations, these chargers are also used to create new Fast Charging Hubs.
Fast chargers and HPC’s are much more complex to install. They require a full solution installation, including advanced study of the site upfront, custom electricity supply from the distribution network operator, installation, and maintenance. TSG Charge is expert in this field and helps you with the installation and future maintenance of fast chargers and HPC chargers. Read more about TSG Charge >
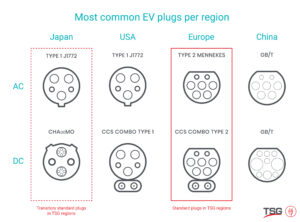
The different type of plugs across the globe
With the introduction of EVs, different type EV plugs were created, depending on electrical network characteristics as well as the current used (AC / DC). This is why there are many variations of plugs across the globe. In the image below, you find the EV charger plugs per region of the world.
In Europe the official standards approved by the European Commission is Type 2 plug for AC charging and CCS 2 for DC charging. CHAdeMO cars plugs are also still found in Europe, but will be reduced over time as most EV manufacturers are moving to CCS European Standard.
EV chargers for commercial fleet or heavy industry
EVs used in a commercial fleet are either passenger cars (such as a taxi fleet) or e-Vans (for last mile delivery). Passenger cars or e-Vans are usually charged at their depot centres with dedicated parking spaces, similar to chargers found in public parkings. Usually, such depot centres install a combination between AC chargers and faster DC chargers, with the majority being AC chargers.
However, fleet charging compared to public charging, requires a higher number of chargers to be installed, which has a significant impact on the complexity of installation. Such as: the sizing of the local LV electrical network as well as the connection to the local electrical Distribution Network Operator. Often the addition of a new point of connection, of a transformer or even of an electric substation may be necessary. As an expert in the field, TSG can advise you in defining the right solution for your fleet.
For heavy vehicles, such as e-Buses or e-Trucks, DC Ultrafast chargers are recommended. Next to that, there are two specific type of chargers that can be very useful: pantograph chargers and mobile chargers.
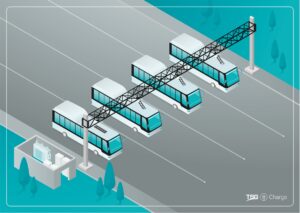 An example of a pantograph charging solution for your fleet.
An example of a pantograph charging solution for your fleet.
Pantograph chargers
A pantograph charger is a powerful charger (up to 450kW) that connects with the vehicle on top of its ceiling. The biggest advantage of a charger like this, is that it works more efficiently. The e-Bus or e-Truck is placed beneath the charger and the connection is made automatically with the charger above. The driver saves time as he does not have to get out of the vehicle to connect the charger.
Mobile chargers
A mobile EV charger can be compared to a power bank for your mobile phone. Mobile EV chargers are chargers you can take with you on transport to charge your vehicle at any time, to ensure long journeys can always be completed. Mobile chargers are quite new and are used in the heavy transportation industry in combination with a dedicated DC charging infrastructure.
Add EV chargers to your site with the help of TSG. Find out what we can do for you!
With over 50 years of experience, we are the European leader in responsible mobility solutions, in which E-mobility plays a huge role. Our TSG Charge team builds E-mobility solutions that fits the needs of your business as well as your customers.
We take care of the installation project from A to Z. We plan, design, build, deploy, and commission the entire EV charging infrastructure. Furthermore, our skilled technicians are always just around the corner to perform maintenance, corrective as well as preventive.
Our Charge experts advise you on which type of chargers fits your business the best, how many chargers you can install on your site, on what location chargers are best placed, and which specific local requirements or regulations you should take into account. Creating the best e-mobility experience, and together with our customers, enabling a more sustainable world.



